Venturing Insights #11 - Corporate Venturing in the AI Era
Let's explore how AI is reshaping corporate venturing strategies.
Previously on Open Road Ventures: in the last episode of Venturing Insights, we asked ourselves some interesting questions: Can AI thrive as both a feature and a product, or will one eventually dominate? Is AI as a product merely something related to the recent AI hype? If you missed it, find out more here!
Welcome to the latest edition of Open Road Ventures! In this episode, we continue with the AI thread, exploring how AI is transforming corporate venturing and the dynamic between startups and incumbents in this rapidly evolving landscape.
The Explosive Growth of the AI Market
The market for artificial intelligence grew beyond 184 billion U.S. dollars in 2024, a considerable jump of nearly 50 billion compared to 2023. This staggering growth is expected to continue, with the market racing past 826 billion U.S. dollars in 2030.
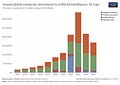
The chart above looks at corporate investment in AI over time, by investment type.
Until recently, private sector investment was relatively low. But, especially from 2018 onwards, it has increased rapidly. Corporate Investments in 2021 were about 30-times larger than just eight years earlier.
This trend has been also seen for VC investments in AI.
The Generative AI Revolution
Specifically, Generative AI is the big deal in this context. According to NFX, the AI revolution can be seen in three waves:
Wrappers Around AI Models: Early movers create user-friendly interfaces around existing AI models, leveraging marketing and sales to gain early market traction. Companies like Jasper exemplify this phase, using strong sales and marketing to lead the market.
Generative AI Inside: Companies integrate AI to enhance their products and services without selling AI directly, gaining competitive advantage. This wave includes businesses using AI to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance quality, often with a focus on customer-centric solutions. A prime example is Spotify, the popular music streaming platform. While Spotify doesn't market itself primarily as an AI company, it has seamlessly integrated advanced AI algorithms into its core product to enhance user experience and provide value.
Visionary Applications: Innovators leverage AI to create new market experiences, fundamentally rethinking industries. These visionary companies will use AI in unprecedented ways, similar to how smartphones transformed the taxi industry with apps like Uber and Lyft.
Fast, Cheap, and Weird: The New Mantra
Integrating insights from Elliott Parker, CEO of venture studio High Alpha Innovation, we see that big corporations need to embrace "fast, cheap, and weird" experiments to stay competitive.
Unlike startups, corporations are optimized for efficiency and predictability, which can stifle innovation. To overcome this, companies should run numerous small-scale experiments, allowing for rapid learning and adaptation. This approach encourages a culture of resilience over pure efficiency, essential for long-term success.
This agile experimentation complements the Corporate Explorer mindset, fostering a culture of continuous innovation and allowing large companies to better compete with nimble startups in the AI-driven market.
Startups vs. Incumbents
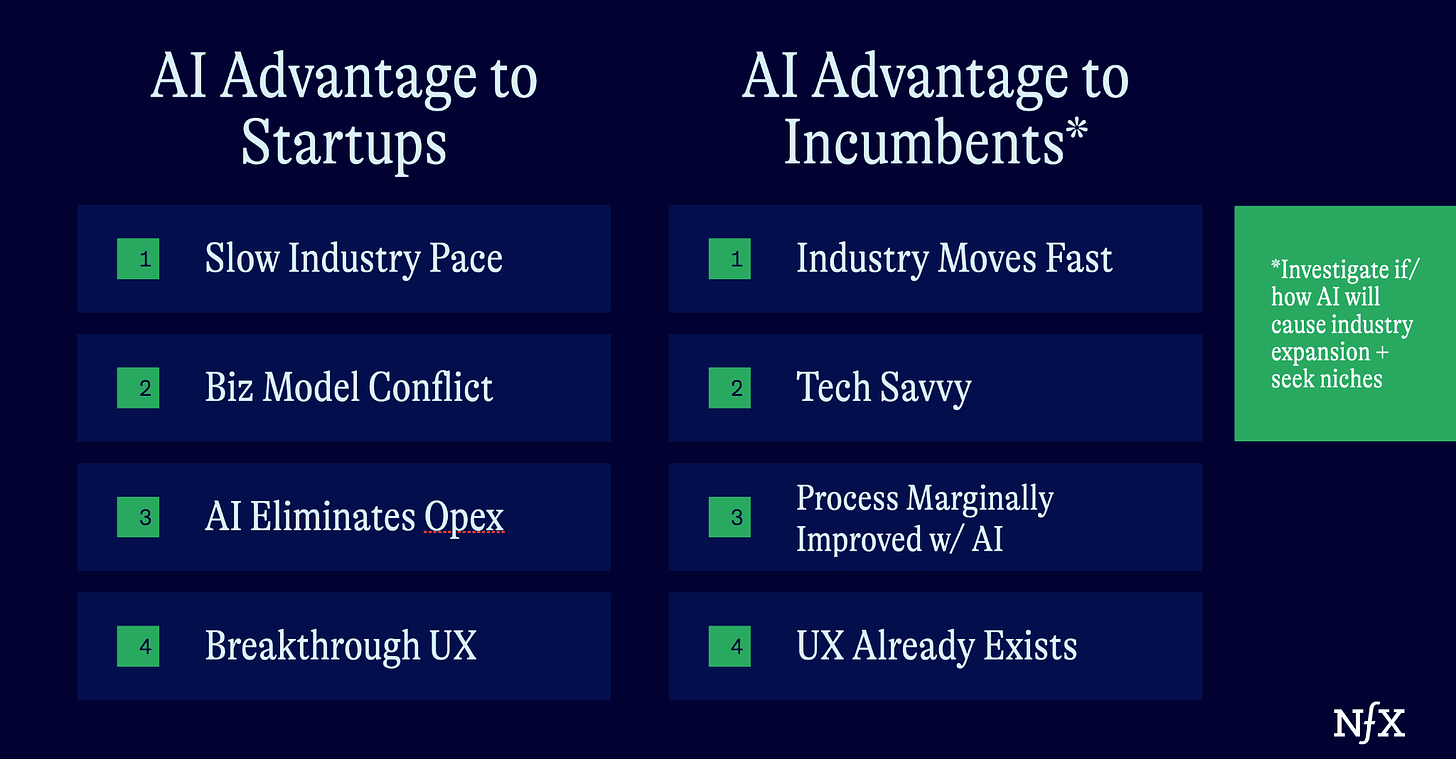
The competition between startups and incumbents in AI is intense, with each having unique strengths and challenges. According to NFX:
Incumbents: Established companies like Google and Microsoft leverage extensive data, resources, and brand recognition to sustain innovation. They can apply AI to existing operations, improving products and services without fundamentally changing their business models. For example, using AI to enhance ad targeting or improve customer service represents sustaining innovation.
Startups: Startups, on the other hand, are more agile and focused. They can outmaneuver incumbents by targeting niche markets with innovative solutions. Startups are often hyper-focused on specific customer needs, using their agility to iterate quickly and develop unique products. Disruptive innovation from startups can create entirely new markets or significantly alter existing ones, much like how Uber and Lyft disrupted the traditional taxi industry by introducing new supply and a different customer experience (AI Periscope).
Most startups deploying AI believe the technology is truly disruptive to their chosen industry. However, to truly harness AI's disruptive potential, a product or service must satisfy two conditions:
It must unlock something previously impossible or unimaginable
It must be challenging to replicate.
If these conditions are met, the startup can leverage AI’s disruptive qualities. Otherwise, startups can still succeed through other innovative paths, as execution is more critical than the idea itself.
Corporate Explorers: Building New Ventures
What Corporates should do in this context? Adopt the Corporate Explorer mindset, fostering internal ventures to innovate and capture new markets.
This approach involves identifying new business opportunities, leveraging corporate assets, and nurturing entrepreneurial talent within the organization.
Successful corporate explorers often adopt several strategies:
Investing in Early-Stage Startups: Corporations are investing in promising AI startups, recognizing that the next generation of unicorns will likely emerge from this space. Early-stage investments allow corporations to tap into innovative solutions and integrate them into their ecosystems.
Creating Dedicated Innovation Units: By establishing separate innovation units, corporations can focus on disruptive projects without the constraints of the core business. These units operate with a startup mentality, promoting agility and experimentation.
Collaborating with External Partners: Partnerships with universities, research institutions, and other companies can drive AI innovation. Collaborative ecosystems enable sharing of knowledge, resources, and expertise, accelerating the development and deployment of AI solutions (NFX).
AI Internal Innovation: Key Challenges and Strategies
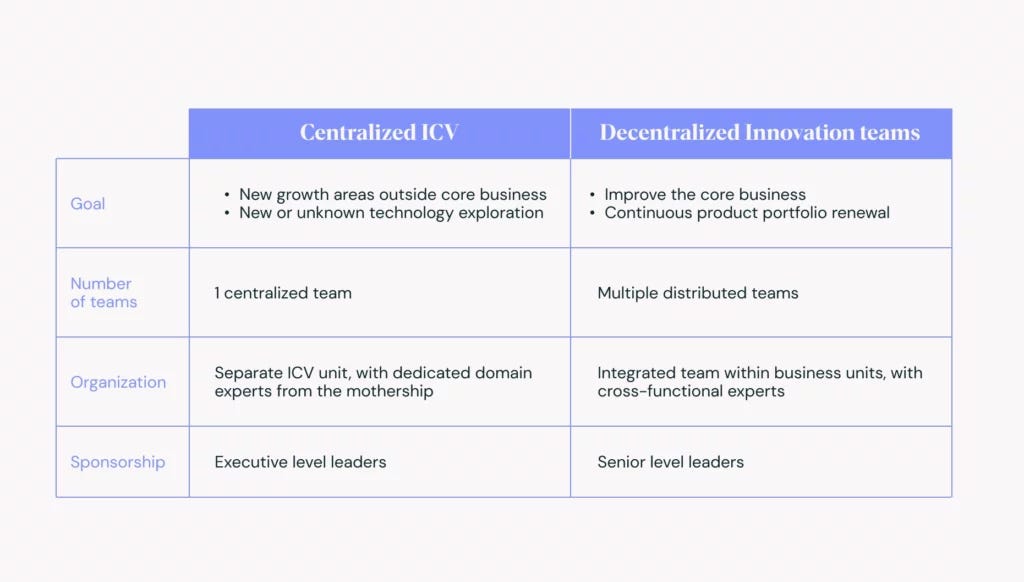
Let’s focus on Internal Innovation now. Board of Innovation explored two common approach to internal innovation: Centralized Internal Corporate Venture Units and Decentralized Innovation Teams.
They also outlined the common pitfalls across sectors like agriculture, aviation, energy, and industrial materials. Here are the key challenges and solutions:
Unclear Direction and Strategy:
Decentralized efforts can scatter resources and dilute focus. A centralized approach with a clear mandate and senior leadership involvement is crucial for improving core offerings and exploring new innovations.
Pressure to Integrate:
Overemphasis on re-integrating internal corporate ventures (ICVs) into the core business can lead to resistance and failure. Clear accountability, performance metrics, and the option to spin out can ensure growth and impact.
Restrictive Internal Policies:
Internal policies often slow down innovation. Creating subsidiaries for autonomy or systematizing exceptions can expedite approval processes while maintaining essential risk management.
Insufficient Resourcing:
Innovation efforts often lack adequate staffing and incentives. Full-time resources, appropriate incentives, and real entrepreneur mentorship can significantly enhance ICV success.
Mid-Level Leadership Challenges:
ICVs take an average of ten years to deliver ROI, often outlasting BU leaders' tenure. Prioritizing market fit and investing in 'patient money' can help overcome this challenge.
The Future of Corporate Venturing
As AI continues to evolve, corporate venturing will play a crucial role in driving innovation and maintaining competitive advantage. Companies that embrace AI and foster a culture of exploration and innovation will be better positioned to capitalize on the opportunities presented by this transformative technology.
At Open Road Ventures, we are excited to witness and report on these developments. Stay tuned for more insights and stories on how AI is reshaping the corporate venturing landscape.
For more detailed analysis and examples of companies leading the AI revolution, check out the full articles on NFX, Forbes, carta, Our World in Data, Board of Innovation and Global Venturing.